Digital Micromirror Device: A Revolutionary Technology
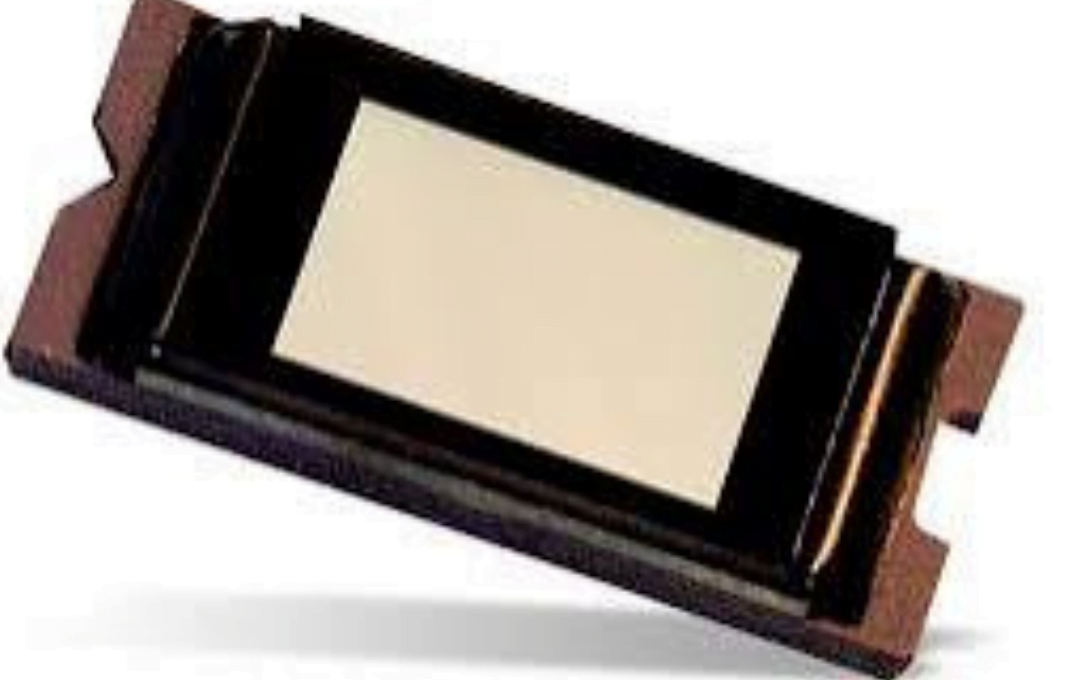

The digital micromirror device (DMD) is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way we experience visual media. Developed by Texas Instruments, the DMD is a core component in digital light processing (DLP) projectors, cinema projectors, and other advanced display systems. This innovative technology has paved the way for high-quality, energy-efficient, and cost-effective visual solutions across various industries.
Read: Leveraging Microlearning in Employee Training Videos
The Digital Micromirror Device
At the heart of the digital micromirror device lies an array of microscopic mirrors, each measuring only a few micrometers in size. These mirrors are arranged in a grid pattern and can tilt individually, either towards or away from the light source. By precisely controlling the tilt of each mirror, the DMD can modulate the light, creating a high-resolution image that is projected onto a screen or display.
Key Features of the Digital Micromirror Device
The digital micromirror device boasts several key features that make it a standout technology:
High-Speed Operation
The DMD is capable of operating at extremely high speeds, with each mirror capable of tilting up to 5,000 times per second. This rapid response time allows for smooth, flicker-free images and enables the DMD to handle fast-moving content with ease.
High Contrast Ratio
The DMD’s ability to precisely control the tilt of each mirror results in a high contrast ratio, which is essential for delivering deep blacks and vibrant colors in projected images. This feature is particularly important in cinema projectors, where a high contrast ratio is crucial for an immersive viewing experience.
Energy Efficiency
Compared to traditional projection technologies, the digital micromirror device is highly energy-efficient. By precisely controlling the light, the DMD minimizes energy waste and generates less heat, reducing the need for bulky cooling systems and lowering overall power consumption.
Applications of the Digital Micromirror Device
The versatility of the digital micromirror device has led to its adoption in a wide range of applications:
DLP Projectors
The most common application of the DMD is in DLP projectors, which are used in homes, offices, and educational settings for presentations, entertainment, and education. DLP projectors offer high-quality images, long-lasting bulbs, and compact designs, making them a popular choice for various applications.
Cinema Projectors
The digital micromirror device is also a key component in modern cinema projectors, enabling the display of high-resolution, high-contrast images on the big screen. The DMD’s ability to handle fast-moving content and deliver a high contrast ratio makes it an ideal choice for cinema projection systems.
Medical Imaging
The digital micromirror device has found applications in medical imaging, particularly in the field of ophthalmology. DMD-based systems are used for retinal imaging, allowing doctors to diagnose and monitor eye conditions with greater precision and accuracy.
The Future of the Digital Micromirror Device
As technology continues to advance, the digital micromirror device is poised to play an even more significant role in the future of visual media. Researchers are exploring ways to further improve the DMD’s performance, such as increasing the number of mirrors and enhancing their tilt accuracy. Additionally, the DMD’s versatility has led to its application in emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), where its ability to precisely control light is crucial for creating immersive experiences.
Conclusion
The digital micromirror device is a remarkable technology that has transformed the way we experience visual media. Its high-speed operation, high contrast ratio, and energy efficiency have made it an essential component in a wide range of applications, from DLP projectors to cinema projectors and medical imaging systems. As technology continues to evolve, the DMD is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of visual media, enabling new and innovative applications that push the boundaries of what is possible.