Types Of Home Heating Systems (2024 Guide)
Introduction to Home Heating Systems
Home heating systems are essential for creating a comfortable living space during colder months. There are various types of heating systems to choose from, including forced air, radiant heat, hydronic, steam radiant, and geothermal systems. Each system has its own unique pros and cons, and it’s crucial to compare them to find the best option for your home.
What are Home Heating Systems?
Home heating systems refer to the equipment or systems used to heat a residential building or home. These heating systems work by converting some type of energy source into heat, which is then distributed throughout the home.
Importance of choosing the right system
Choosing the right heating system for your home is crucial, as it can affect your comfort, energy bills, and even your home’s resale value. Different heating systems may be more efficient, cost-effective, or environmentally friendly depending on your location and housing situation. By comparing the different types of heating systems, you can find one that matches your needs and preferences. Consulting with local HVAC experts can also help you determine which system is the best fit for your home.
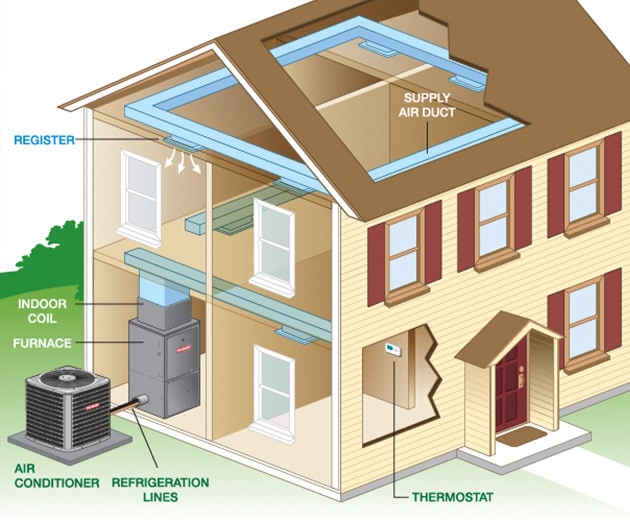
Gas Furnaces
Gas furnaces are one of the most common types of heating systems, fueled by natural gas or propane. They work by igniting gas in the burner and producing hot combustion gases that pass through a heat exchanger, transferring heat to the air circulated through the ductwork. The furnace starts when the thermostat detects the need for heat, and gas supply flows into the furnace through a gas valve. Gas furnaces are cost-effective, widely available, and heat homes faster than electric furnaces. Some potential downsides include higher upfront costs, maintenance needs, and potential safety risks associated with gas appliances.
How Gas Furnaces work
A gas furnace operates by igniting natural gas which creates a flame in the burner. αντλίες θερμότητας The hot combustion gases from the flame pass through a heat exchanger that transfers the heat to the air. The heated air then circulates through ductwork to heat the home’s interior. The furnace operation begins when the thermostat detects the need for heat and signals the furnace’s electronic controls to open the gas valve and turn on the ignition system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gas Furnaces
The advantages of gas furnaces include being cost-effective, efficient, and widely available, as natural gas is a common utility in many regions. Gas furnaces also heat homes faster than electric furnaces, making them ideal for colder climates. However, gas furnaces require safety precautions and regular maintenance to prevent gas leaks and ensure proper operation. Potential downsides include higher upfront costs, potentially shorter service life, and fluctuating gas prices. Ultimately, whether a gas furnace is right for a home depends on factors like heating efficiency, cost-effectiveness, adaptability, and maintenance costs.
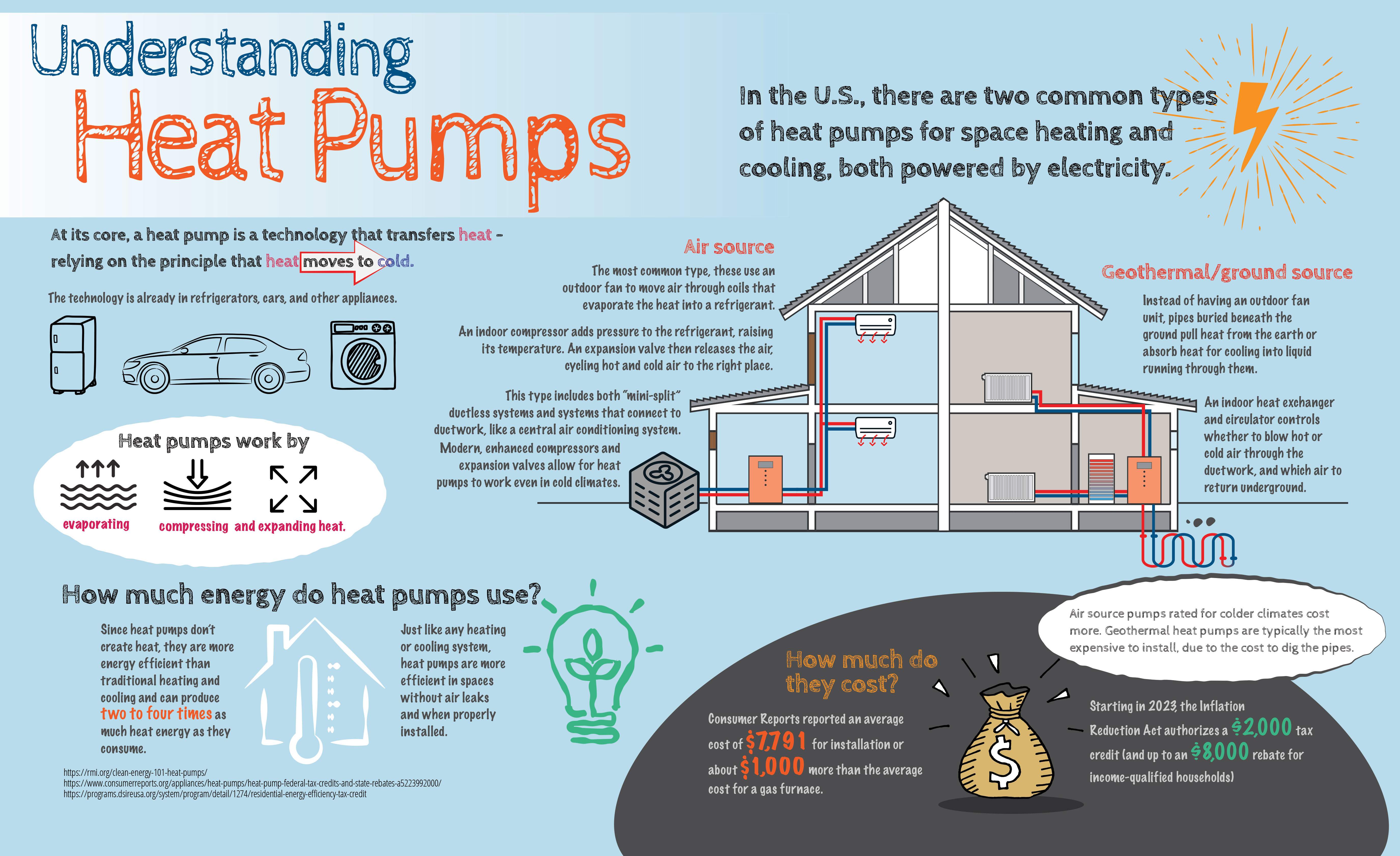
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps work similarly to air conditioners but have the added benefit of providing heat during colder months. There are two main types of residential heat pumps: central heat pump systems and mini-split ductless heat pump systems. Central heat pumps are the most common type found in Ontario homes. They work by extracting heat from outdoor air and transferring it inside through a refrigerant, warming the air circulated through ductwork. Mini-split ductless heat pump systems operate similarly but don’t require ductwork and can provide zoned heating and cooling.
How Heat Pumps work
Heat pumps move heat from one location to another using refrigerant. In heating mode, outdoor air is drawn into the heat pump and transfers heat to the refrigerant circulating within. The warm refrigerant is then compressed, raising its temperature further, and transferred inside to warm the air circulating through ductwork or directly into designated zones with mini-split systems. In cooling mode, the process is reversed, and the heat pump removes heat from indoor air to send it outside.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are energy-efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. They use less energy than traditional HVAC systems, reducing utility bills and carbon footprint. Additionally, heat pumps can provide both heating and cooling, eliminating the need for separate systems. However, heat pumps may struggle in extremely cold temperatures, and the initial cost of installation can be more expensive than a traditional AC unit. Proper installation and maintenance are essential to ensure proper operation and longevity. Ultimately, choosing a heat pump will depend on factors like climate, home size, and lifestyle.

Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces are an option for homeowners who prefer not to use gas or oil for heating. These furnaces have an electrical heating element that warms the air before circulating it throughout the house. The thermostat controls the furnace operation, turning it on and off according to the desired temperature.
How Electric Furnaces work
Electric furnaces work by running an electrical current through a heating element, which creates heat. The furnace’s blower motor then circulates this warm air throughout the house via ductwork. The unit kicks on and off as needed to maintain the desired temperature, as indicated by the thermostat.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Furnaces
One advantage of electric furnaces is that they are typically less expensive to purchase and install than gas furnaces. Additionally, they have a longer lifespan, often lasting up to 30 years with proper maintenance. Electric furnaces are also easier to operate and maintain, as they do not require fuel storage or combustion safety inspections.
On the other hand, electric furnaces have higher operating costs than gas furnaces, making them less cost-effective in the long run. They may also struggle to heat homes in extremely cold temperatures, and relying on electricity for heating can lead to higher utility bills. It is important to weigh the pros and cons carefully before deciding which type of furnace is best for your home.

Oil Furnaces
An oil furnace is a heating system that burns fuel oil to generate heat for your home. The combustion of fuel oil occurs in a chamber, and the resulting heat is transferred to air passing through the heat exchanger. The heated air is then circulated to different parts of the house, allowing for temperature regulation.
How Oil Furnaces work
Oil furnaces utilize a dedicated storage tank that stores the oil until needed. The oil flows to the furnace through a piping system, where it is burned in the combustion chamber. The heat generated by the combustion is then transferred to the air passing through the heat exchanger. The warmed air is blown via a blower motor through ductwork, distributing it throughout the house.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Oil Furnaces
Oil furnaces were once a popular choice, mainly because they were cheaper to buy and lasted longer. They are commonly used in colder climates such as the Northeastern United States. However, they are less efficient compared to gas furnaces and may be more expensive to operate due to the higher cost of oil. Also, oil furnaces may need more maintenance and repairs over time compared to electric furnaces due to the combustion process and moving parts. Nevertheless, oil furnaces remain a viable heating option for homeowners who live in locations where gas is not available.
Join the conversation and contribute your valuable content through our partners at Accessily.com